Introduction
Finding the best hydrophilic coating should be achieved through performance testing on lubricity, durability and particulates.
- The product’s intended application and substrate material construction can help determine if UV or Thermal cure coatings are the best fit.
- UV and Thermal cure coatings differ in production curing times and batch sizes.
- Your coating vendor will help you identify the best curing option for your device.
For medical device companies who are developing interventional products to support life-saving procedures, the selection of a hydrophilic coating plays an integral part in the performance of the device. Today’s hydrophilic coatings must exhibit three criteria to qualify as acceptable for use: high lubricity, high durability and low particulates to ensure that the device will meet the testing requirements from global regulatory agencies such as the FDA and EMA.
To apply a hydrophilic coating to a medical device, there are two primary methods used to dry and cure the coating: ultraviolet (UV) light and thermal heat. The selection of the curing methodology depends on several factors, including throughput, coating durability, space in the manufacturing location, curing equipment, market application and the substrate of the device. This article will review the differences between UV and thermal heat cure coatings to support your decision-making when selecting a hydrophilic coating.
Understanding a Hydrophilic Coating Application
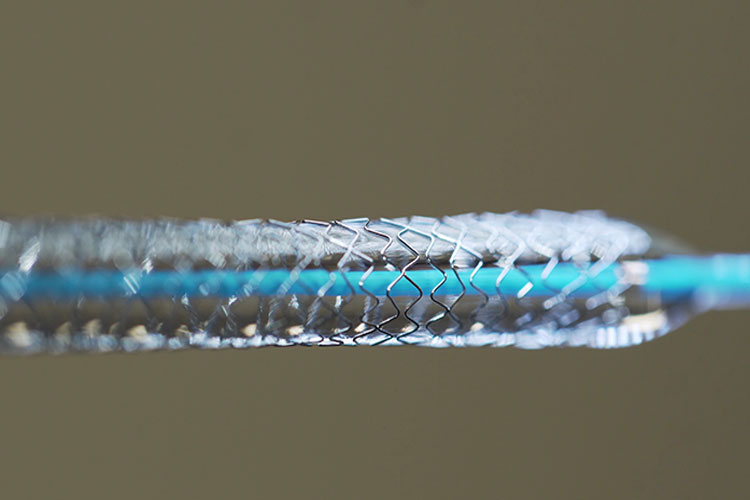
The lubricous (slippery) nature of hydrophilic coatings makes them ideal for medical devices. They allow the device to easily traverse the vasculature, avoiding possible puncture damage to vessel walls and eliminating abrasion between the device surface and the vessel walls. Hydrophilic coatings are most often used in, but not limited to, neurovascular, cardiovascular, peripheral vascular, ophthalmic, urological, and gastroenterology applications.
At Biocoat, we encourage our customers to analyze three major factors that measure the effectiveness of a hydrophilic coating. These factors are:
- Lubricity: The property that describes how slippery a surface is, i.e., the value of its coefficient of friction
- Durability: The strength of the coating that allows it to withstand the duration of procedure without degradation
- Particulates: The measure of the amount of foreign materials that are left in the body after the device is used in the procedure
Choosing Between Ultraviolet (UV) Light and Thermal Heat Cure Coatings
One of the important questions when choosing a hydrophilic coating is which type of curing will be employed for the application of the coating to the device. UV cure has traditionally been the popular choice, but thermal heat offers a different set of benefits. Biocoat is one of the only hydrophilic coating providers to offer industry-leading performance in both UV and thermal heat cure coatings.
Biocoat’s HYDAK® coatings are applied via a bi-laminar platform using a base coat and a topcoat. The hydrophobic base coat is used to normalize the substrate material and to prepare the surface for the application of the hydrophilic topcoat. The base and topcoats are chemically bonded, which ensures an extremely durable coating adhesion and minimizes the release of particulates into the body.
Overview of Market Applications by Curing Method
Biocoat’s HYDAK® coatings have been successfully used in therapeutic areas that are not listed in the above chart. Should you have an unlisted requirement, please be sure to contact us to learn more about our capabilities.
Comparison of Coating Batch Sizes and Curing Times
“We needed a coating partner that not only has a good coating, but can handle everything we throw at them.”
Chief Executive Office | Neurovascular Medical Device Company
Other Factors to Consider
At Biocoat we typically recommend to our customers to let the performance of the coating determine the better cure option. However, there are times where we will recommend one option over the other. Some examples of this include:
- Inner diameter coating capabilities: The coating of the inner diameter is a unique capability for thermal cure coatings. The coating of the inner diameter can enable the use of thinner substrate materials that can improve distal reach and overall device performance.
- Matching in-house coating equipment: When the company’s manufacturing facility already has a certain type of coating equipment in place, we recommend that the same cure option is used in future project development.
- Curing processes may require certain curing types: For certain substrates there may not be a choice in which curing option is used. As an example, during the coating of hydrophilic films, there is a benefit to have the films in a centralized thermal oven to ensure an even curing process.
- Device substrate requirements: Heat-sensitive substrates may require UV cure systems in order to avoid altering the properties of the materials used in the device. In other cases, UV light may discolor the base material, and in this case, a thermal cure coating is the best option.
Conclusion
Choosing between UV or thermal cure coatings depends on many factors, and your coating provider will be able to guide you to the benefits of each system. As one of the only providers that can offer industry-leading performance in both UV and thermal heat cure coatings, Biocoat is able to guide you to the best solution for your project’s needs.
A Review of Biocoat’s UV and Thermal Cure Performance
Figure 1 demonstrates the lubricity and durability of our HYDAK® technology. The Biocoat R&D team purchased six different commercially available angioplasty catheters, one of which was coated with Biocoat’s Thermal Cure technology. To compare the performance between Biocoat’s UV and Thermal cure performance, a test substrate using the UV cure was also included in the analysis. We measured both the lubricity and durability of each of the microcatheters to determine where HYDAK® performance compares in relation to industry competitors. Our testing proves that HYDAK® exhibits “best-in-class” lubricity and durability results. The pinch test method used was silicone-pads and 470 g load with PBS at 37C.
As illustrated in Figure 2, the Biocoat R&D team purchased seven different commercially available neurovascular microcatheters, three of which were coated with Biocoat’s HYDAK® Thermal Cure technology. The Biocoat team measured the number of particulates generated from each of the catheters to determine where HYDAK® performance stands in relation to industry competitors. Our testing proves that HYDAK® coatings exhibit best-in-class lubricity and durability results. Catheters were cycled through an ASTM F2394 stent retention tortuous pathway.
Do you have a project that requires a hydrophilic coating?
Contact us today to learn about Biocoat’s industry-leading coatings!
+1 215.734.0888
sales@biocoat.com